
1.6K
Downloads
33
Episodes
The Social Mind Center presents the ”different skill notebook” a tool that provides strategies to build social-emotional skills resulting in social competency. Since March our world has experienced many changes with the COVID pandemic. Change is the new constant in our daily lives. Requiring us to be adaptable and adjust to the changes daily. The different skill notebook is a life curriculum for you to equip your child with the skills to communicate, connect, and build relationships for life. We want our children to have success beyond academics by acquiring skills to adapt, cope, self-manage and find purpose in life.
Episodes

Sunday Feb 09, 2025
Listening First: Transforming Relationships Through Play
Sunday Feb 09, 2025
Sunday Feb 09, 2025
Welcome to the Different Skill Notebook Podcast, hosted by Ana Anselma, a smart parenting tool empowering families with vital life skills. In this episode, Ana delves into a transformative approach at the Social Mind Center's Brick Club, where listening first strengthens relationships with neurodivergent and autistic individuals. Reflecting on years of experience, Ana shares how listening and removing expectations create an environment where trust and connection thrive.
Listen to inspiring stories of new members like Brian, who overcame past challenges and embraced active participation through the thoughtful and flexible orientation process at Brick Club. Anna reveals how enabling these individuals to take the lead reduces anxiety and fosters engagement and learning.
This episode highlights the importance of connecting before teaching and how trust paves the way for meaningful interactions with children. Gain insights on ensuring parents and children feel welcomed, understood, and respected without the pressure of performance during their first visit to the Brick Club. Discover the powerful impact of listening and choice-making in nurturing a supportive and inclusive community.
https://www.socialmindcenter.com/different-skill-notebook-blog/listen-to-neurodivergent

Monday Jun 10, 2024
Unveiling Social Communication Challenges in Autism
Monday Jun 10, 2024
Monday Jun 10, 2024
Welcome to the Different Skill Notebook Podcast, hosted by Ana Anselma, co-owner of the Social Mind Center and an educational consultant. In this episode, Ana delves into the crucial topic of social communication and autism, exploring why it's essential to equip neurodivergent individuals with the skills to communicate their thoughts, needs and desires more effectively.
Ana shares insights from her extensive experience, including the consistent narratives from parents seeking help for their children who struggle with social communication despite years of behavioral therapy. She highlights the gap in the school system's approach, which often focuses on minimizing behaviors rather than building communication and self-advocacy skills.
Through the story of the Social Mind Center's inception and its mission to provide real-time interaction and practice for children, Ana emphasizes the importance of teaching social communication skills. She outlines the strategies and approaches used at the center, such as social groups, modeling, and understanding the perspectives of individuals on the spectrum.
Join Ana as she provides valuable insights into social communication, its significance, and practical ways to support neurodivergent individuals in developing these vital skills. Stay tuned for the next episode, where she will discuss cognitive flexibility and its role in perspective-taking.
For additional information, definitions, and references, visit the blog at socialmindcenter.com. Feel free to comment or ask questions on the different skill notebook blog, and Ana will be happy to respond.
Thank you for tuning in, and we look forward to our next podcast!

Sunday Aug 27, 2023
Adulthood with Autism Part 2: What Finding Support can Mean
Sunday Aug 27, 2023
Sunday Aug 27, 2023

In this episode, Melissa Pascucci shares her success finding and pursuing a profession she loves. Melissa shares the steps she took to help find her new career. Melissa never stopped attending events at her school, Marino Campus. She participated in all professional and community events hosted and promoted by the Dan Marino Campus.
She emphasizes the importance of pursuing learning and growth. She says that one must stay connected to the community. Attending events helps you to make new connections with people that can help you find a career that is your passion. Melissa also stressed the importance of volunteering to obtain experience and exposure.
Melissa connected with a mentor, Gabriella Procci, whom she met through a program Dan Marino Campus had started called the Academy. The Academy offered continuing education for graduates of the Dan Marino program. This mentor encouraged Melissa to pursue working with the neurodivergent population.
Gabrielle recommended Melissa for an internship at the Social Mind Center. The Social Mind Center had not had this type of internship before; we were sure we could all learn from each other. Melissa started as a paid intern at the Center, coming several days a week to assist in social communication groups. She would shadow Dr. Savinelli in social groups. It modeled running a social group, which requires lesson planning, teaching strategies, and promoting opportunities for the kids to engage and connect.
There is also the part of managing the sticky situations that arise. Melissa learned to help children/teens to cope with stressful situations. Melissa also became a moderator with the Brick Club (Brick-by-Brick Programme). Becoming a moderator for Brick Club required her to complete a course and additional hands-on training running a group.
The internship gave Melissa a preview of what a career working with a neurodivergent community may be like. It allowed her the opportunity to experience teaching and managing a group. We both agreed that the best possible experience to determine your career path is exposure to different opportunities to observe and work in a field of interest, as an intern or even a volunteer.

Monday Aug 21, 2023
Adulthood with Autism Part 1:Finding our place and purpose in the world
Monday Aug 21, 2023
Monday Aug 21, 2023
In this episode, Melissa shares her journey after high school to find her place and purpose in the world. Her employment experiences and career ambitions. Her story is one of perseverance and hope.
She expresses the need for autistics to be consistently exposed to different experiences and opportunities. This helps them to figure out what may be the best fit for them. She says independence for autistics requires their parents to allow them to do life their way. There are multiple pathways to finding one's place and purpose in life. Parents must believe in their children's ability to find their way.
Autistics may need more time and different opportunities to find their path. Melissa was candid on how parents can be too controlling and struggle to listen and respect their autistic young adult as an individual—respecting that they may have different desires than you. Also, to respect that they may know autism best, so their perspective and voice matter.
Melissa continues to advocate for herself and her students. She deeply desires to help autistic people find a career they love and self-realize. As an advocate, she believes in and encourages her students.
She emphasizes how parents can support new experiences, listen, and respect their young adult.
In our next episode, Melissa will share her internship at the Social Mind Center and her new career.
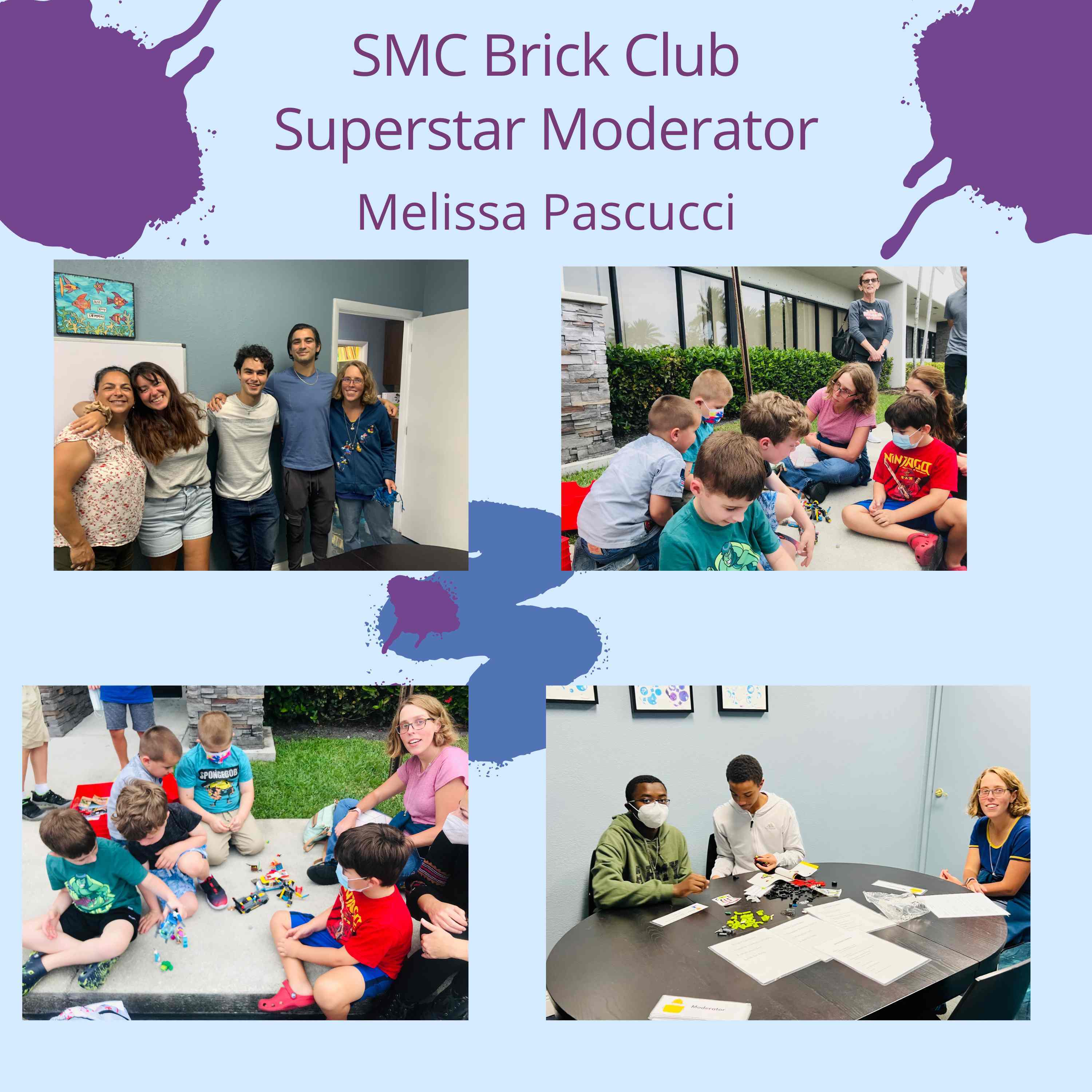

Monday May 01, 2023
Appreciating the Autism Mind
Monday May 01, 2023
Monday May 01, 2023
Before the term neurodiversity and neurodivergent came to be, I used the term autism mind. My son taught me 18 years ago that autism was a different kind of mind. He had a different process in which he approached his daily life. I realized the strategy was to equip him to navigate the neurotypical world. I taught him how the neurotypical world worked. How does the world work, and what does it expect of you? I taught him the neurotypical perspective, and he showed me the autism mind perspective. My most appreciated aspect of his process was to take breaks. From age three, he understood what he needed; he just needed words to express his needs. His process and pace influenced mine. I learned that you can still get plenty done at a slower pace. Thanks to him, I changed my pace and learned to live in the moment rather than my days defined by a list of tasks.
We bridged the gap between his process and the neurotypical expectations with strategies to help them adapt. There is more than one pathway to learning and living. Both Gaby and Nick needed strategies to help them navigate their school days. Gaby required more information to manage her anxiety, and Nick needed breaks throughout the day to sustain attention and stay on task. Eventually, Gaby learned to locate the additional information she needed, and Nick learned to get through the day without breaks.
We devised ways for them to meet their needs and work through the neurotypical expectations. And it was okay if they could not meet the neurotypical expectations, especially when the NT person was dealing with had no compassion and was highly rigid. Together we learned different ways to get things done. We learned together. I hope the information in this episode will help you help your child thrive.
More often than not, my children would not meet the neurotypical expectations. Amazingly enough, you can still thrive without meeting neurotypical expectations.


Sunday Feb 05, 2023
When I first heard the word autism
Sunday Feb 05, 2023
Sunday Feb 05, 2023

Seventeen years ago was the first time I heard the word autism. This episode shares the events that lead me to seek an evaluation for my son. How did I know my son needed an evaluation? What did I do when I heard the word autism?
This series of episodes will discuss the start of my journey in seeking to know autism. Reflecting on what I have learned from my children and thousands of other children. This past year, I believe there has been a significant pivot in my perspective in advocating and educating autistics to be independent and self-realize their dreams. Ana Anselma

Friday Sep 30, 2022
When should I consider medication to manage anxiety?
Friday Sep 30, 2022
Friday Sep 30, 2022

In this episode, Gaby Anselma joins us again to continue our conversation on anxiety. We discuss medication as a tool to deal with anxiety symptoms. Some of the other points discussed in this episode:
- Medication is a tool, not a total solution to anxiety management.
- When do you decide to take medication?
- What are some of the symptoms or signs that lead one to consider medication?
- clouded thinking
- frozen and unable to act
- What are some of the symptoms or signs that lead one to consider medication?
- How can medication help you?
-
- Stop the extreme symptoms and
- Allow you to explore the source of your anxiety more and use coping strategies to manage your anxiety
- Understand that some of us are wired to worry
- Help you understand how your thinking drove my anxiety
- How I would self-sabotage my tennis game
What was your breakthrough for you in managing your anxiety?
- Understanding that your thinking can heighten your anxiety
- Sometimes our anxiety is physiological. Your body is anxious outside of your thinking
Do you believe medication helped you gain the skills to manage your anxiety effectively?
When did you stop taking medication?

Tuesday Aug 09, 2022
To medicate or not medicate your child/teen?
Tuesday Aug 09, 2022
Tuesday Aug 09, 2022

Considering medication for your child is a serious decision. In this episode, we discuss the different factors and considerations involved.
1. Does your child/teen struggle with?
- Attending or focusing
- Anxiety
- Self-regulation - organizing mind and body to achieve goal-directed behavior
- Emotional regulation
- Irritability
- Impulse control
- Cognitive inflexibility- restrictive behaviors
- Depression
2. Do these symptoms impact their quality of life and ability to navigate daily activities?
- Most notably, are these symptoms/behaviors a barrier to learning?
3. What is the intensity and frequency of the symptoms impacting your child?
4. What systems are in place in your child's home and learning environment to help minimize these symptoms and struggles?
- 0rder, structure, and predictability
- Consistency
- Individual Education Plan IEP
- Smaller classroom
- Individualized instruction/tutoring
- Interventions/coaching focusing on skills to cope and manage symptoms
5. Journal as many details relating to the symptoms and the impact on daily activities. Specifically, document the frequency and intensity of symptoms and behaviors.
- Have someone else observe your child in the classroom to assist you in gathering data.
6. Consult with either?
- Behavioral Pediatrician
- Psychiatrist
- Neurologist
7. Pursue diagnostic evaluation with a psychologist to seek the source of symptoms and behaviors.
Spending some time reflecting and examining the information from the above list can help you make a more informed decision. Sometimes the answer to improving your child's quality of life and learning is more related to implementing systems, building coping skills, and altering their environments. Medication is a tool that should be combined with other tools to increase success. Medication is not a tool that teaches skills. It alleviates barriers to learning.

Thursday Jul 14, 2022
Healing and Managing Anxiety in College by Gaby Anselma
Thursday Jul 14, 2022
Thursday Jul 14, 2022
Healing and Managing your Anxiety!
This is our second episode in the series of Anxiety Management. In this episode Gaby discusses what her anxiety looks like now in college. She has dealt with anxiety most of her life. In every season it looks different.
Gaby discusses what her anxiety feels like and how it impacts her thinking and effectiveness on a daily basis. Then she details for us 5 different strategies that have helped her cope with the anxiety.
Understanding whether your anxiety is significantly impacting your quality of life is an important place to start. Gaby also discusses the importance of seeking help to make this determination as anxiety impacts your clarity of thought.
Gaby shares how counseling has helped her understand her anxiety throughout her life and how to manage it to have a more fulfilling life.
Please join us as we explore anxiety management in teens and young adults.

Tuesday Jun 21, 2022
What is the most important social skill?
Tuesday Jun 21, 2022
Tuesday Jun 21, 2022
WHAT IS THE MOST IMPORTANT SOCIAL SKILL?

When I think about our work at the Center teaching social competency, there are many layers to teaching these skills. For those who have social communication skills come easy. We never give much thought to what it feels like for those who struggle with social, emotional, communication, and self-management skills.
If I were to pick one most important skill in developing social competency, that would be turn-taking. All socialization and communication is a back and forth. Children with social competency difficulties can struggle with this with fundamental skills. There is no social interaction that does not require turn-taking.
Social-emotional reciprocity is the back and forth interaction that takes place in communication. (Norris, 2018)
We take a social approach to have conversations with others, and we share our interests in our discussions. Part of that social-emotional reciprocity is knowing how and when to initiate or respond to others' social interactions (Norris, 2018).
Some of the skills necessary to engage in social-emotional reciprocity include:
-
Waiting for a turn to speak in school or meeting
-
Talking to someone
-
Making eye contact
-
Demonstrating something
-
Writing a note, email, etc.
These are all examples of back and forth in communication and social situations. Turn-taking and waiting are fundamental skills to navigate every day in our communities. Turn-taking should be incorporated into all teaching as it is essential to social competency (Norris, 2018).

Skill: Turn-taking
In the Anselma home, we focused on turn-taking daily. In prioritizing helping Nick develop communication, we sat and played every day. The play was part of so many aspects of our home life as turning-taking is part of all play. The underlying foundational turn-taking skills are cognitive flexibility (transitioning -shifting mindsets), thinking of others (perspective), and impulse control.
Start by playing what they love to play or doing what they love to do.
Strategy:
Turn-taking takes much practice for all kids. There is no clarity as to when it will be their turn. I prefer to take a favor, and/or my turn then your turn. Often the word sharing is used; however, for kids with weaknesses in social communication, sharing can be a more abstract concept. It's a bit more precise.
A foundational component of communication and socializing is taking a turn. It is not a conversation or playing if there is no turn-taking/back and forth.

Build:
Consistently and repeatedly model turn-taking and thinking of others. There is a why to turn-taking: we need to think of others. It is perspective-taking thinking of others' thoughts and emotions. The family unit is the first social group your child will encounter.
-
When my kids were young and during our teen years which we are still in, I would say "your turn" to pick the restaurant, activity, or game.
-
When my kids were toddlers and early elementary, I would join in whatever they were doing, and then I would ask them can I have a turn now.
-
With homework, I would help them by doing a problem or sampling/modeling the task so they could see it being done.
-
I would say can I help you get started, then I would say now it is your turn; you continue. I would also get things started and let them finish.
-
Our family often traveled, so we would say your turn to pick a place to eat or visit since you accompanied us on our adventure. We would take turns on whose activity would go first in the day.
-
For siblings, one child mustn't control the family. That you take turns with their requests.
When they are young, it needs to be more literal and physical, as if you would pass a ball back and forth. As they become preteens and teens, you need to discuss more the thinking of others. I constantly shared my perspective with my kids and what the other person's perspective may be. It was a three-part exchange:
-
What am I thinking and feeling about this situation?
-
What are you thinking and feeling about this situation?
-
What do you think they are thinking and feeling about it?
It is developmentally appropriate to be self-centered during the teen years, so requiring your kids to take a turn is even more critical. You cannot allow your home to become child-centered. You must help them acknowledge all family members and that they have preferences as well.
Social media does not help with monologues since they can have a one-way conversation all day. I frequently see parents letting young children and teens monopolize the conversation. They never redirect or say, " Let's hear what your friend has to say.

Social turn-taking and sharing space:
When my kids were having difficulty sharing space or engaging with us. I would join them and sit there for a while with them so that they grow accustomed to me in their area.
-
sharing space in close proximity is vital to establish joint attention (paying attention to the same thing)
-
Ask to look at what they are looking at or doing
-
use the language "my turn" and "your turn."
-
give them a turn when doing anything together, even if they don't ask for it
-
Some children or teens have difficulty turn-taking when in situations where the environment is unfamiliar, or many people. In these situations, the child/teen feels that they have less control which may make them feel extremely uncomfortable. In these situations, they will seek to take control, and the response may not always be socially expectable. Their reaction may be to engage their peer group, disrupting play or conversation abruptly. They intend to join in, but the sudden abruptness disregards peers' space and exchange. The best way to help your child/teen ease into these situations is to teach them to observe. Before participating one can be an observer.
-
When entering a social situation, practice with them entering, greeting, waiting, looking, and observing before jumping in.
-
the greeting is important sets the tone, and asking questions, "what are you all up to"
-
practice observing, listening, and imitating before joining situations so that you can model for them
-
provide information on expectations and what are some exit options if they do not feel comfortable or need a break
-
When your child mentions that they are having difficulties with peers, gather information on how they approach and engage peers. Commonly, they may not be waiting their turn and this causes conflicts with peers.
Practice conversational turn-taking with your child as often as you can. Model asking about their day, needs and challenges. Share about your day, needs and challenges. Spend time listening and be a part of their moment or interests especially with teens.
Listening and observing in the teen years is important because there is so much going on in their environment. They may need help navigating this new season in their life, and they may not know how to ask for the assistance they need. I find they need much coaching on what to say and when to say it. Self-advocacy is very important in the teen years, learning to speak up for yourself and your needs.
Works Cited:
K. Norris, BS, MEd, Autism Basics, July 24, 2018. The excerpt was taken from this course answering the question What is social-emotional reciprocity.
Resource:
This entire excerpt was taken from Norris's Autism Basic's course
Let's examine some foundational skills that underlie these methods of information sharing.:
Joint attention. One of the basic skills involved in social-emotional reciprocity is joint attention. This typically develops in the first year or two of life. Joint attention is actively paying attention to the same object or activity at the same time with another person. We see babies do this all the time. As you're holding a baby, for example, and he hears an airplane in the sky and sees you look up, he'll also look up to see what it is. He may point at the airplane and look back at you, wanting you to look back at that. This tends to be a skill that children with autism are missing. The lack of joint attention may be one of the early signs of autism.
Imitation. Imitation is another basic skill for social-emotional reciprocity. Parents, teachers, and peers are all people that young children will imitate. Imitation is one of the ways that children learn. If children with autism have that break in that social-emotional reciprocity, if they have that break in that ability to imitate others, then their social communication is negatively impacted.
Reciprocal engagement. Once we have joint attention in place and we have imitation in place, then we usually enter into that reciprocal engagement. Again, it's the back and forth that we need to maintain long enough to learn something, enjoy something, and share something with another person. It's paying attention to people versus paying attention to objects. Children with autism have a tendency to focus strongly on objects. Objects are much more predictable than people and much easier for them to understand because of the deficits in their social communication.
Non-verbal communication. Another area that can be affected in social communication is non-verbal communication. This would include facial expressions, as well as tone of voice. Using a single finger to point to an object is a non-verbal gesture that's important for young children to develop. You'll see very young children indicating what they want by pointing to it. They'll look at the object and then they'll look back at their caregiver to say, "Hey, pay attention to this. This is what I want. I'm pointing right at it." This often happens even before they can tell you the name of the object. Eye contact is a significant part of non-verbal communication and is often something that children with autism will try to avoid. Maintaining eye contact with someone is very uncomfortable for them, mainly because of that gap in their social and communicative abilities. We need to teach them ways that they can use their gestures or behaviors so that they can communicate their wants, their needs, and their interests.
This Ask the Expert is an edited excerpt from a course entitled, Autism Basics.
Kimberly Norris, BS, MEd
Kimberly Norris has been an educator for more than 25 years. She received a master's degree in elementary education with an emphasis in reading from Southeast Missouri State University. She has provided training for early childhood educators on topics ranging from developmentally appropriate practice to adaptations for children with special needs. Presenting both at state and national conferences, she is passionate about educating professionals in the field of early childhood education.
